Cracks can make otherwise transparent materials like glass nontransparent by making it move semi-randomly in many directions. If light enters material with different refraction index and different local speed of light then it bends somewhat and cracks
For transparency material shouldn't have cracks and scrapes larger than the wavelength of visible light (around 0,5 micrometers).
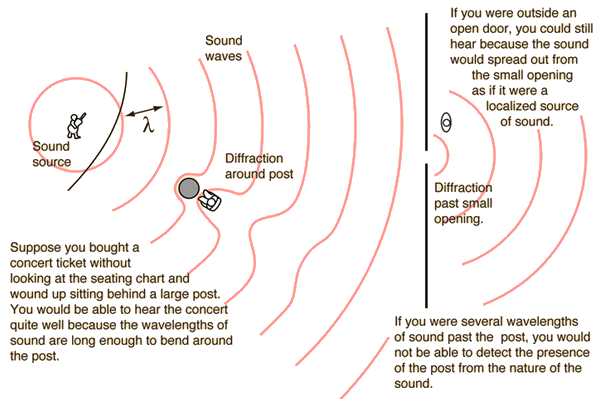
Light sound waves visible light waves also bend around things that are shorter than wavelength so within couple of wavelength waves straighten out and continue behind small objects. That's also the reason why radio waves used in radars have to be smaller than object to detect it and x-rays with wavelength similar to molecules can make molecular structure visible.

No comments:
Post a Comment